Out of the 80% of adults who receive some sort of medical care per year, 40% (or 2 in every 5 patients) have experienced some sort of medical error. These patients who have experienced such medical errors often have negative views surrounding healthcare and are less likely to recommend the healthcare facility to a family member or friend.
With patient satisfaction, experience, employee satisfaction, and healthcare reputation management at the forefront, finding ways to reduce the likelihood of medical errors is necessary for the health of the industry and, of course, the patients served.
Costs associated with medical errors result in billions lost per year. So what are the common medical errors, why do they happen, how do we avoid them, and most of all, how can nurses help prevent these errors? Let’s find out.

Table of Contents
- What are the Most Common Medical Errors?
- What are the Different Types of Medical Errors?
- What Causes Medical Errors?
- The Cost of Medical Errors in the USA
- How Does a Nurse Prevent Medical Errors?
- 9 Tips to Prevent Medical Errors in Nursing
- Ask for clarification
- Utilize other staff and supervisors as resources
- Complete hourly patient rounding
- Practice the 4 P’s of purposeful rounding
- Document, document, document
- Report any adverse events to a supervisor
- Watch out for abnormal vital signs
- Limit your overtime
- Closed-loop communication
What are the Most Common Medical Errors?
Below is a list of some of the most common medical errors from a 2022 report by Thomas L. Rodziewicz, Benjamin Houseman, and John E. Hipskind: Medical Error Reduction and Prevention.
-
Adverse drug events
-
Premature discharge
Premature discharge from inpatient hospital settings can lead to readmissions and increased hospital costs. In return, this also increases the burden on the staff to treat more patients, especially when it could have been avoided. Oftentimes this is due to missed abnormal vital signs (AVS) and lack of communication on behalf of the staff, the patient, and friends or family.
-
Burns
-
Equipment Failure
This can include improper training for staff in executing of using medical equipment, equipment malfunction, and equipment failure.
-
Failure to provide prophylactic treatment
In Greek, the word “Phylax” means “guard.” Prophylactic treatment is intended for proactive measures to prevent disease or infection. For example, an antibiotic may be administered as a prophylactic treatment after surgery to prevent infection.
-
Patient Falls
In a healthcare setting, falls are often attributed to blood loss, medication side effects, low blood sugar, altered mental state, environmental changes, urge to use the restroom, and decreased strength & balance.
-
Medication side effects
-
Improper Transfusions
-
Misdiagnosis, delay in diagnosis, or failure to utilize the appropriate test or act on a particular laboratory result
Diagnostic errors can occur for three main reasons: a delayed diagnosis, an incorrect diagnosis, and a missed diagnosis. A diagnostic error can be defined as the failure to either establish an accurate and timely explanation of the patient’s health problem(s) or communicate that explanation to the patient.
-
Mistaken patient identities
-
Ulcers
-
Preventable suicides
-
Restraint-related death
-
Surgical injuries
-
Under and overtreatment in administering treatment (i.e., dosage)
-
Wrong-site surgery
What are the Different Types of Medical Errors?
There are two main types of medical errors: errors of omission and errors of the commission.
Errors of Omission
This form of error is caused by the failure to act or actions not taken on behalf of the patient. This could be simple or complex. An example would be an understaffed nursing team that can’t answer call bells on time, which leads to an increase in patient falls due to the patient attempting to use the restroom. This error could be due to time restraints, staff limitations, miscommunication, improper hourly rounding, etc.
Errors of the Commission
This form of error is caused by medical staff taking incorrect action in response to an event. This could mean administering the wrong medication, wrong dosages, or not being aware of a patient allergy due to improper communication or reporting.
What Causes Medical Errors?
According to a study by Attia Bari, Rehan Ahmed Khan, and Ahsan Waheed Rathore (2016), Medical errors; causes, consequences, emotional response, and resulting behavioral change, medical error causes were evaluated and divided into two main groups: Intrinsic (fault of the medical provider) and Extrinsic (fault related to external sources: staffing, supervision, etc.). It is important to note that the majority of the medical errors examined in this study were minor (48%), while only 18% were considered major.
Intrinsic medical error causes
- Fatigue related to working long hours
- Inadequate experience
- Improper training
- Missed warning signs
- Lack of communication
Extrinsic medical error causes
- Other obligations medical staff had to take care of
- The case itself was complex
- Inadequate supervision
- Procedure complications
- Incorrect lab or test results
When the study analyzed the correlation between medical error causes and behavioral responses, they found that a large majority of those who facilitated a medical error had reactions that were “information seeking” and “vigilance.”
In other words, the medical staff responded to the errors by looking for solutions and gaps such as:
- Needing to seek more advice from seniors and mentors
- Consult with the supervisor more often
- Continue their education/read more materials/shadow more
- Pay more attention to details
- Confirm data and patient journey of care
- Communicate better with patient
- Communicate better with the team
Overworked, understaffed, & lack of communication
In many cases, hospitals and healthcare facilities are experiencing a major employee crisis. Coined the “great resignation” or the “nurse exodus,” many healthcare workers left the field following COVID-19 due to stress, grief, and lack of resources. While many of these studies are pulled from prior to the pandemic, it can only be assumed that the lack of staffing is resulting in overworked employees, putting them at risk of medical errors. Thankfully, due to advancements in research, organizational structure, and digital platforms that are transforming the way healthcare systems communicate- there is an opportunity to grow.
Cost of Medical Errors in the US
Medical errors in healthcare can quickly rack up expenses on behalf of the facility. Here are some studies that examined the cost of medical errors across the United States.
- The Financial and Human Cost of Medical Error… and How Massachusetts Can Lead the Way on Patient Safety (2019)
- Over a 12-month period, 62,000 medical error cases were evaluated. It was estimated that the cost associated with these errors was over $617 million.
- A new, evidence-based estimate of patient harms associated with hospital care (2013)
- Around 400,000 hospitalized patients experience some type of preventable harm each year, which results in an estimated cost of $20 billion per year.
- The economics of health care quality and medical errors (2008)
- Approximately 200,000 patient-related deaths per year are due to some form of medical error. In 2008, the estimated cost for the USA was $19.8 billion.
- The financial impact of patient safety errors (2021)
- Approximately 100,000 patient-related deaths per year result in a $20 billion cost for the US.
Overview of Medical Error Costs
While results from studies may differ and newer statistics are necessary, it can be estimated that the United States experiences nearly $20 billion or more in costs associated with medical errors, resulting in preventable harm to over 400,000 patients and up to 200,000 patient-related deaths. According to a study done by John Hopkins (2018), medical error-related deaths may be as high as 250,000 per year.
Where do the medical error costs come from?
- Lack of reimbursement from insurance companies
- The increased cost associated with attempting to fix medical errors
- Noncompliance with boards can result in fines
- Decreased funding from government-based programs
- Lawsuits
- Employee turnover associated with medical errors
- Harm to the facility’s reputation
How Does a Nurse Prevent Medical Errors?
Nurses and nurse leaders play a significant role in preventing medical errors among patients. At the frontline of healthcare, nurses are tasked with providing exceptional care at the bedside, combining medical expertise and communication/service skills.
Nursing medical errors often involve the following five mistakes:
- Patient falls
- Infections
- Medication errors
- Documentation errors
- Equipment injuries
Referencing the same study, these five mistakes are most often made for the following seven reasons:
Failure to…
- Communicate & collaborate with their team
- Clarify interdisciplinary orders
- Ask for or offer assistance when needed
- Utilize evidence-based performance guidelines
- Properly communicate information to friends and family
- Limit overtime to avoid burnout
- Keep nurse units adequately staffed to be able to safely treat all patients
9 Tips to Prevent Medical Errors in Nursing
1. Ask for clarification
If you’re tasked to care for a patient but are unclear on the patient’s chart, care, medications, procedures, or history, it’s critical to ask for clarification to ensure needs are met with certainty.
2. Utilize other staff and supervisors as resources
As healthcare providers and nurses, you’re not expected to know everything. If you’re in a situation where you may not feel confident or comfortable performing the required level of care, it’s important to reach out to your coworkers and supervisors. Supervisors are there to be a resource to you in times of uncertainty. Since each patient care journey is unique, educating yourself on each patient’s needs is critical to meet them without error.
3. Complete hourly patient rounding
By completing hourly patient rounding, you can ensure that the patient’s needs are consistently met, reducing the need for call bell usage and accidents related to patient falls, medication, and miscommunication between patients, friends, family, and staff.
By using a healthcare digital nurse rounding tool such as Seyzo Health, nurses and nurse leaders can ensure that hourly patient rounding quotas are met and track what needs were met and what will need to be done. With all of the information in one centralized location, you can feel confident that you’re meeting patients’ needs.
4. Practice the 4 P’s of purposeful rounding
By practicing the basic 4 P’s of purposeful rounding during your hourly rounds, you can reduce the risk of patient falls and increase patient satisfaction. The 4 P’s are pain, peripheral IV, potty, and positioning. Always make sure to check in on the patient’s pain level, their IV status, if they need to use the restroom, and if they’re comfortable. In addition to positioning, it’s important to consider the environmental surroundings and ensure there is no trash or hazards in the way of the patient’s mobility.
5. Document, document, document
By properly documenting everything that you do as a nurse, you can ensure that other staff members are up to date with the exceptional care being provided. This avoids any gaps or miscommunication by creating an easy-to-access document where other nurses and medical providers can see what was done and what needs to be done.
With a digital rounding platform like Seyzo Health, you can ensure that every step of the patient journey is properly documented for others to have access to. This communication through documentation reduces medical errors, improves efficiency, outcomes, and increases patient satisfaction.
6. Report any adverse events to a supervisor
In the event that an unfavorable outcome occurs or is to be expected, it’s important to report it to your supervisor as soon as possible. Studies have shown that nurses who have made medical errors deal with shame and occasionally do not reach out to superiors due to this behavioral reaction. Stay on top of things and avoid further errors by telling someone.
7. Watch out for abnormal vital signs
By bringing abnormal vital signs (AVS) to the forefront of patient care, you can prevent adverse outcomes and medical errors related to premature discharge. With a digital healthcare platform, you can manage AVS using artificial intelligence (AI) to make sure your reactions are proactive and not reactive.
8. Limit your overtime
Burnout trails quickly behind with nursing staff shortages causing employees to work ample overtime. Try to limit your overtime to avoid making medical errors associated with burnout and fatigue. Practice self-care at the moment you can, and remember to take care of yourself just as well as others.
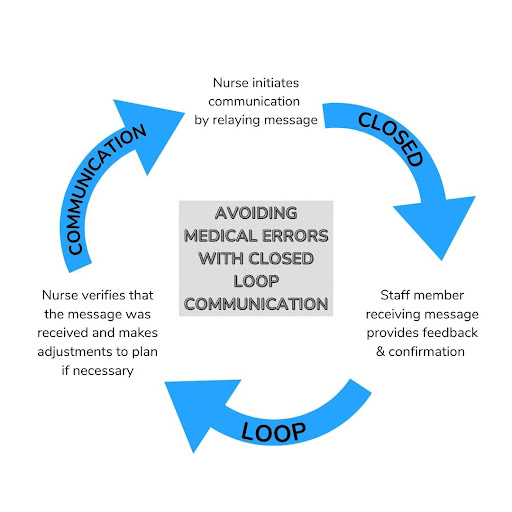
9. Closed-loop communication
By utilizing closed-loop communication, you can ensure that your message gets across to the correct staff members and proper feedback is provided. This way, you are not only better at collaborating with other coworkers, but you are guaranteed to avoid misunderstandings.
Conclusion
Medical errors account for significant costs in the healthcare industry and result in increased patient deaths, staff burnout, and decreased patient satisfaction. By understanding the typical causes of common medical errors, you can take these nine tips and put them into action to prevent medical errors in your facility.




Thanks for your blog, nice to read. Do not stop.